Last Updated on March 6, 2024 by teamobn
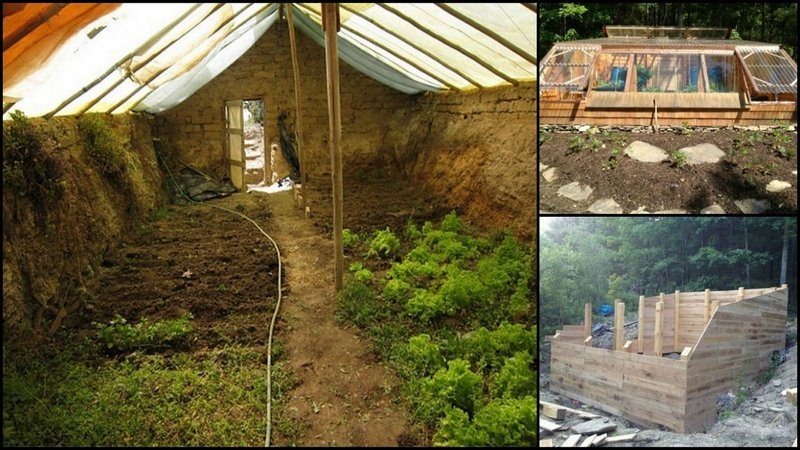

Earth sheltering is a popular method of climatology, also known as geodesy in older literature, and geotechnics in some parts of the world. A greenhouse can be a perfect example of a climatology technique because it is a structure built solely for the purpose of maturing plant products.
Building an earth-sheltered greenhouse is an eco-friendly way of growing plants. This greenhouse is relatively simple to construct and much cheaper than conventional pre-manufactured greenhouses.
Building a sustainable, eco-friendly greenhouse can be most effectively achieved by covering the exterior of the building with soil or sand and insulating it with straw. This will significantly reduce energy costs.

The earth-sheltered greenhouse is energy-efficient, as it uses less energy to heat and cool in the wintertime. It is also aesthetically pleasing, as it looks more modern than the typical greenhouse.
An earth-sheltered greenhouse is customizable – it can be the shape and size that the owner wants.
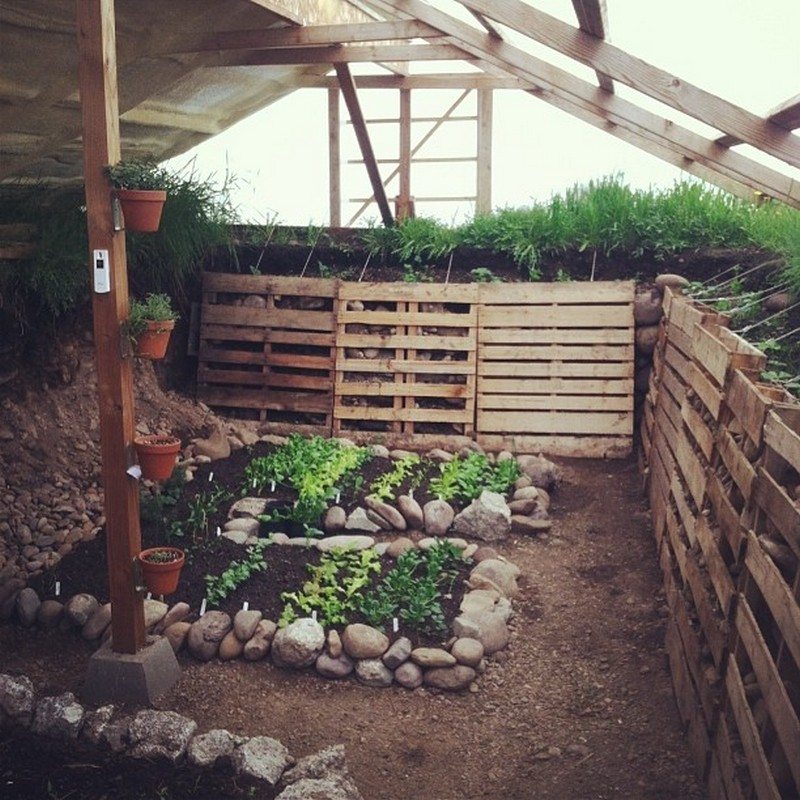

Things to consider in building an Earth-Sheltered Greenhouse
Type of Soil
When deciding whether to build an Earth-Sheltered Greenhouse, the most important factor to consider is the type of soil you have.
This is because if your soil is sandy and porous, there is a greater chance of water seeping into the ground, which could cause the greenhouse to flood when it rains.
Size
It is important to consider the desired size of the earth-sheltered greenhouse you want to build because it will affect the dimensions of the location to place it and the cost of construction.
You may have to spend a lot of money on the greenhouse depending on its size. If it is too small, it could take a while to raise the temperature inside to a suitable level. However, if it is too large, the temperature may stay too warm.
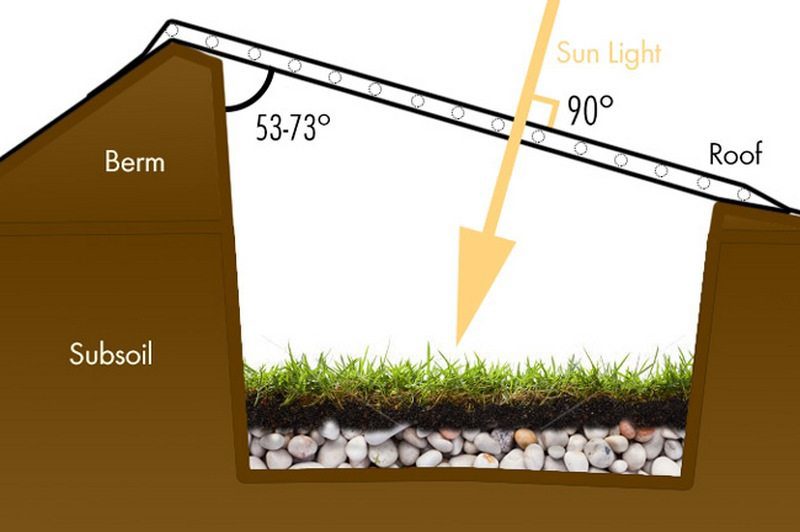
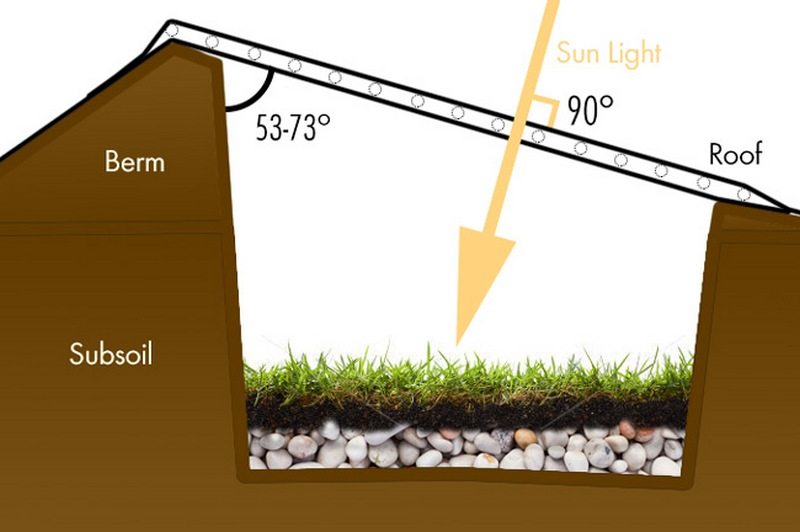
Insulation
The importance of considering the insulation of the earth-sheltered greenhouse is the fact that it will give you the ability to grow your organic produce all year round regardless of the temperature that is outside.
This greenhouse must be properly insulated to function efficiently. The type of insulation material you use is important to consider because different materials provide different levels of insulation and energy efficiency.
Ventilation
Ventilation is extremely important to the earth-sheltered greenhouse owner. In order to maintain proper temperature and humidity levels, a greenhouse must be properly vented or air-conditioned.
Otherwise, the greenhouse could become too hot or too cold, which could lead to the loss of plants due to temperature stress. Ventilation is used to provide additional heat to the greenhouse during the winter and to aid in cooling the greenhouse in the summer.
Since the greenhouse is underground, it is important that you have a way to ventilate it. This is easy to do by making sure you have holes in the greenhouse. The holes should be placed at the top of the greenhouse, where it will naturally ventilate.
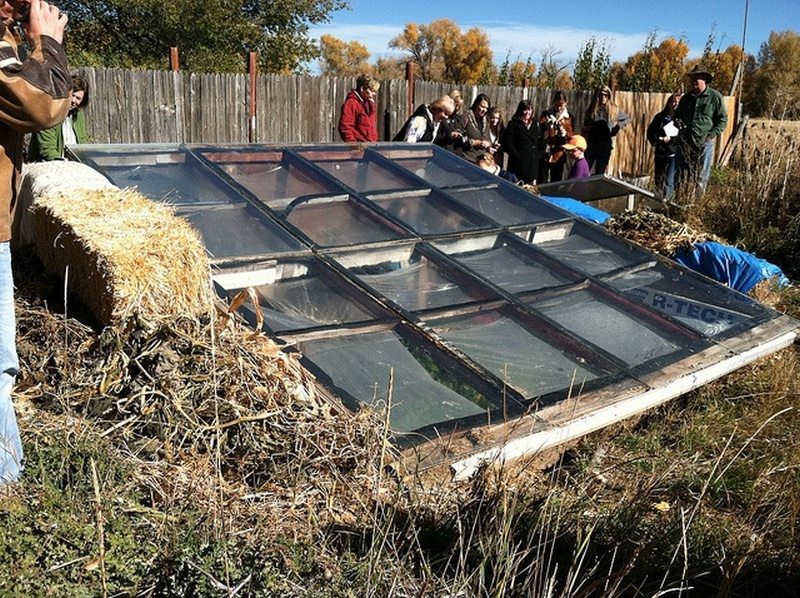

Cost and Quality of the Materials Used
Unlike other structures that are designed for humans to inhabit, earth-sheltered structures are designed to give plants and animals a comfortable place to live.
This is because earth-sheltered structures with their high thermal mass tend to be much cooler than open spaces and are much warmer than areas exposed to the elements.
The quality of the materials used in an earth-sheltered greenhouse construction project is important because they will determine how much you will have to spend to repair, replace or maintain them.
You will avoid the extra cost that comes with the use of low-quality materials and can spend your money on other important things in your life. If you want a more enjoyable growing experience, higher yields, and energy savings, you should buy a more expensive greenhouse made with better-quality materials.
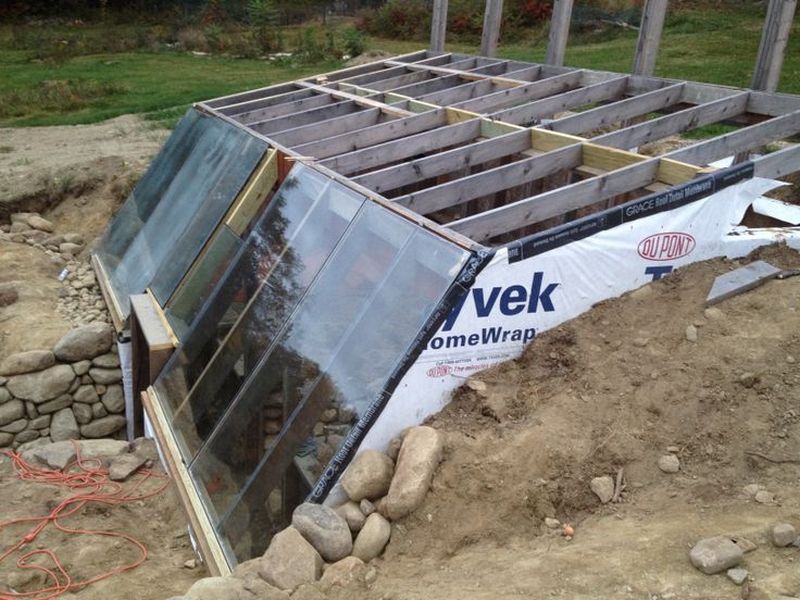

So, what are you waiting for? Plan your desired earth-sheltered greenhouse now!
Click on any image to start the lightbox display. Use your Esc key to close the lightbox. You can also view the images as a slideshow if you prefer 😎
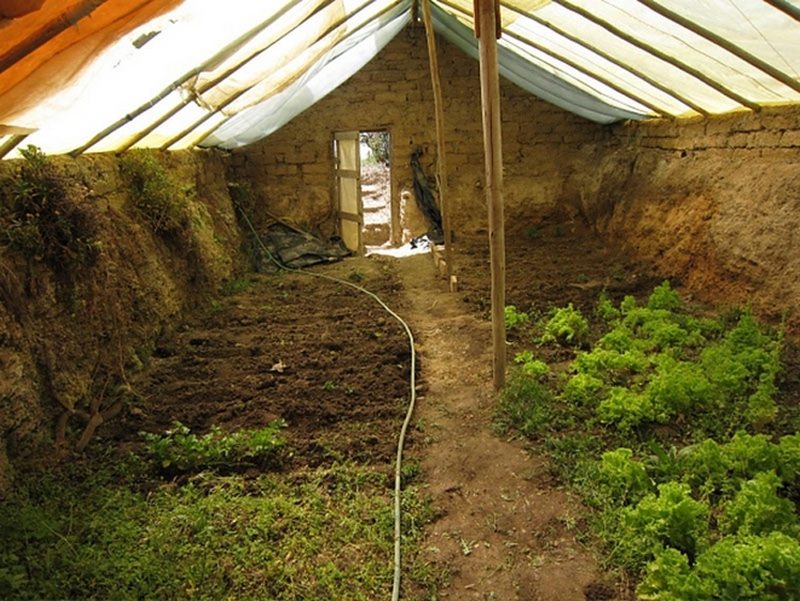
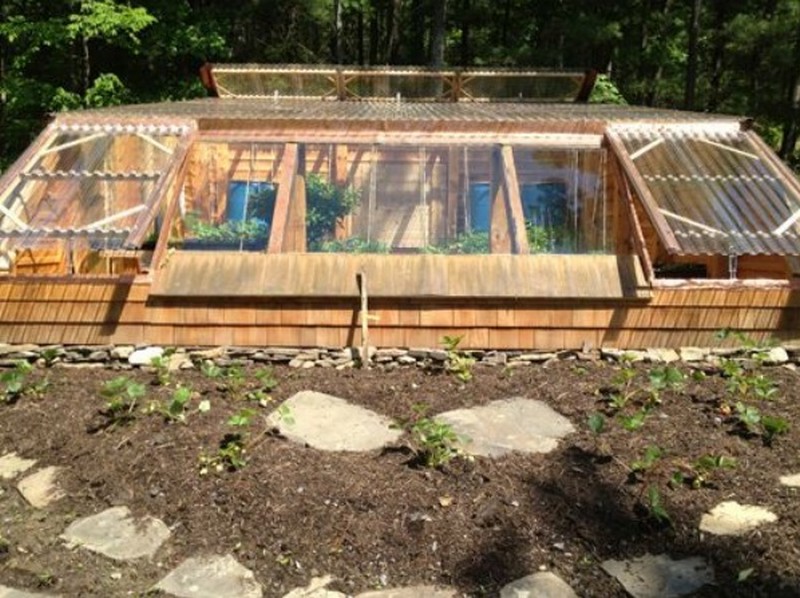
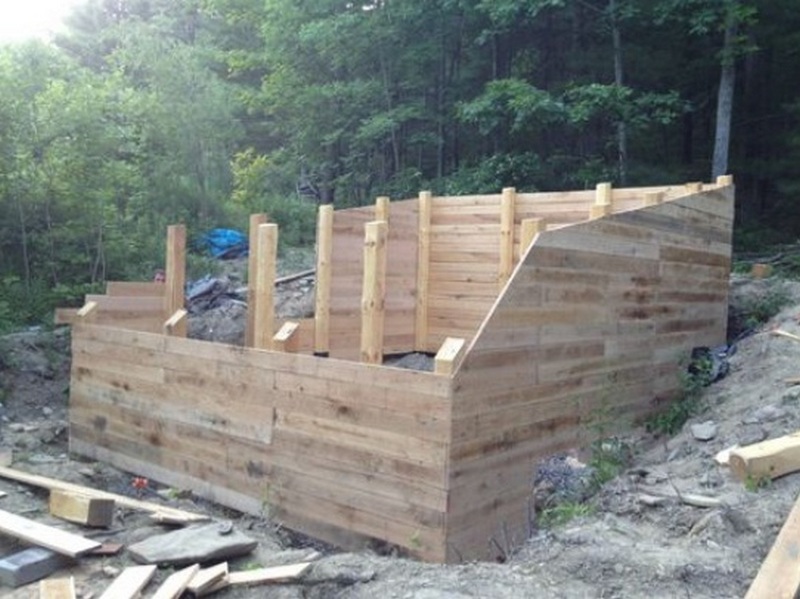
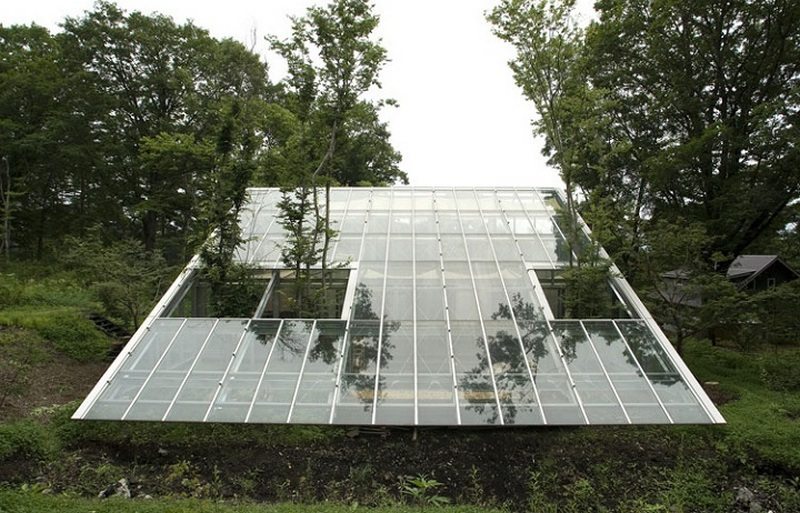
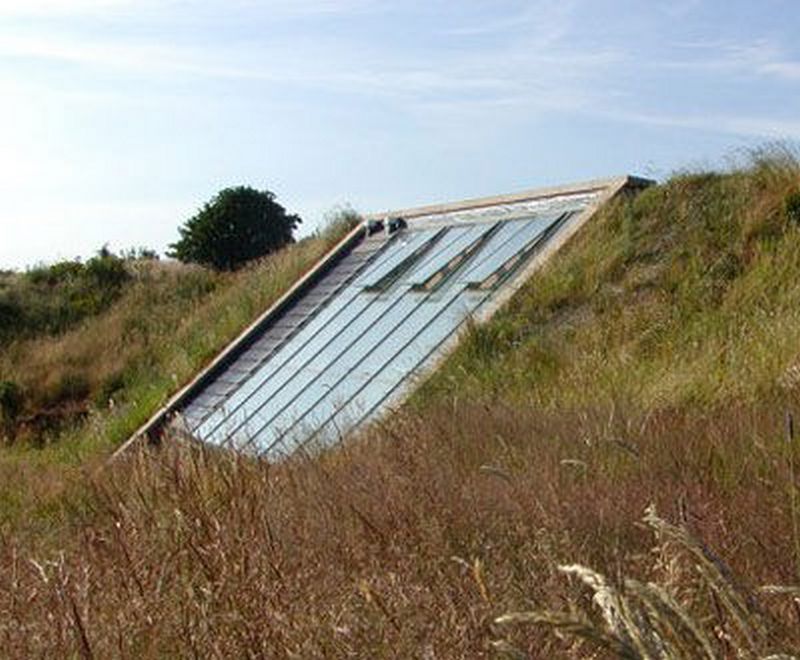
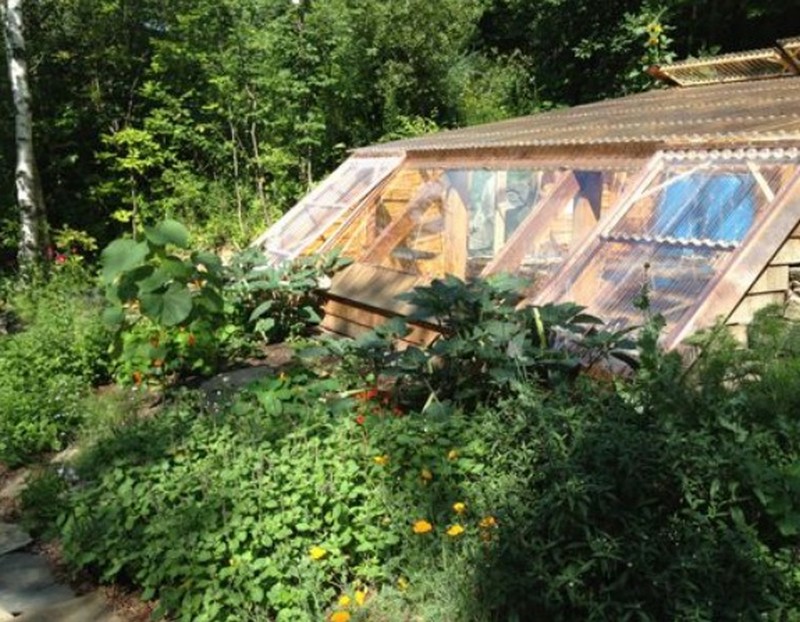
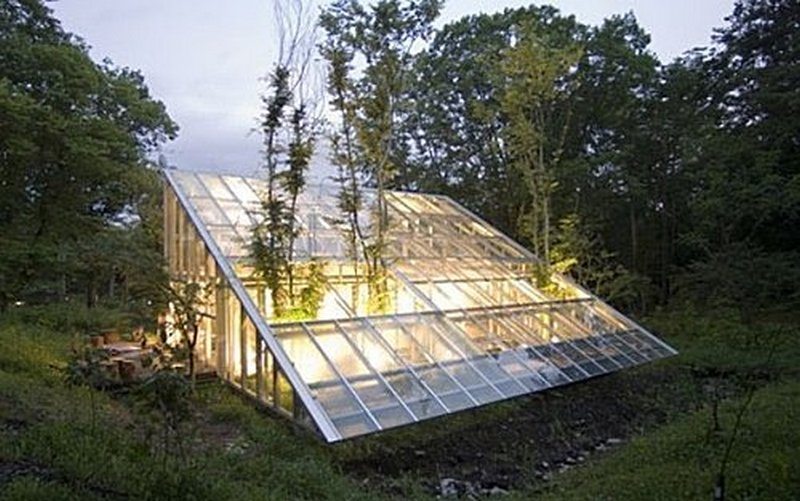
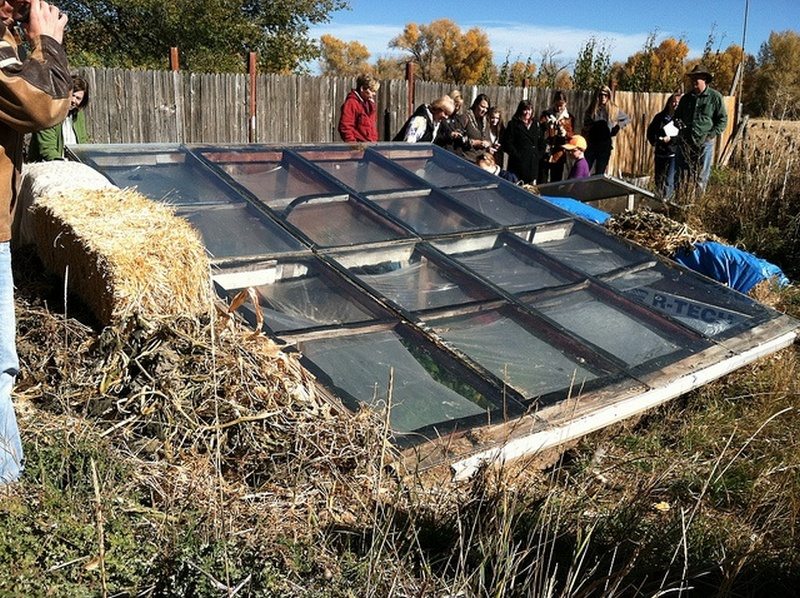
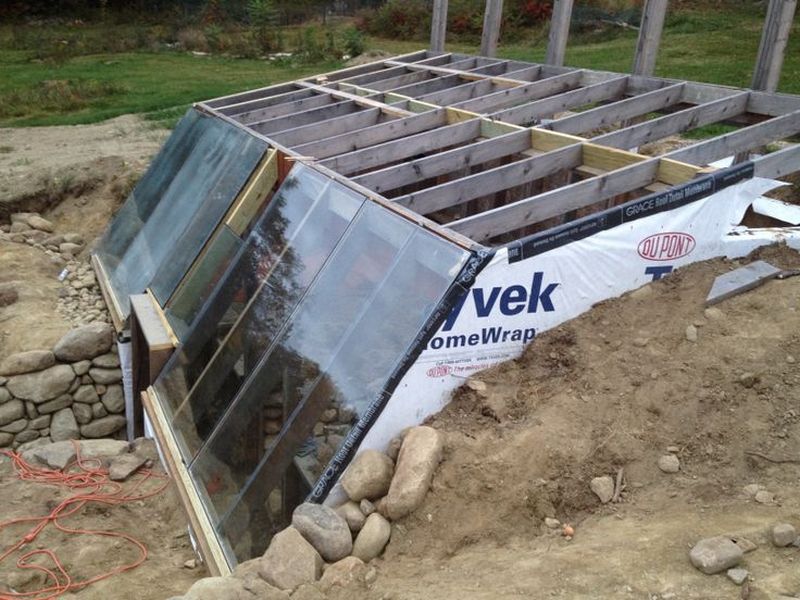
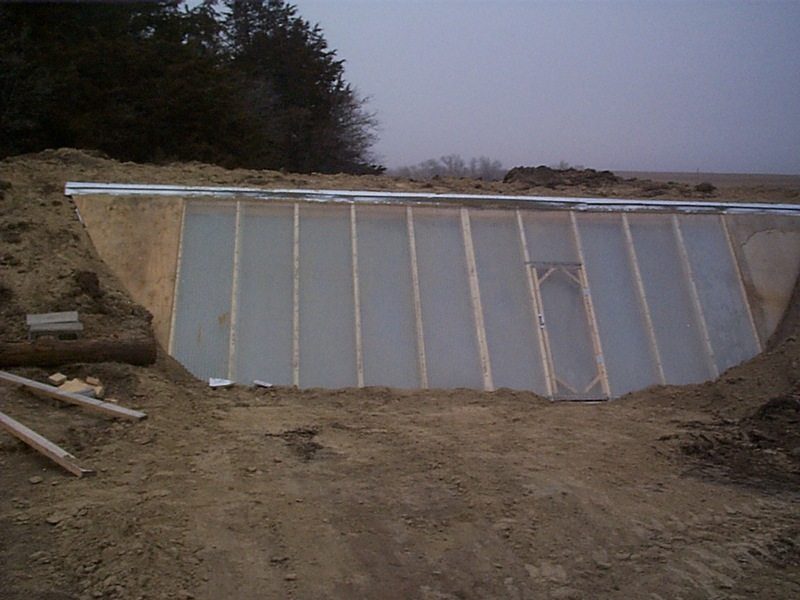











Want to extend your growing season? Why not build an earth-sheltered greenhouse?
If you liked this project, you will also like viewing this DIY greenhouse…
Water Management Techniques
Water management is a critical aspect of maintaining an efficient and sustainable earth-sheltered greenhouse. Given the unique subterranean nature of these greenhouses, addressing water seepage, drainage, and irrigation becomes essential to protect the structure and ensure optimal plant growth. Implementing effective water management techniques can prevent potential issues such as flooding, water damage, and inadequate moisture levels for plants.
This section explores various strategies to manage water effectively in an earth-sheltered greenhouse.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting stands out as a sustainable, eco-friendly approach to water management in earth-sheltered greenhouses. This method capitalizes on the natural precipitation collected via gutters and downspouts strategically placed around the greenhouse’s exterior. The harvested water is then stored in tanks, ranging from simple barrels to more sophisticated cisterns, depending on the scale of the greenhouse operation and the anticipated water needs.
The benefits of rainwater harvesting extend beyond mere water conservation. By utilizing rainwater, earth-sheltered greenhouse owners can significantly reduce their reliance on municipal water systems, which is both cost-effective and environmentally responsible.
Moreover, rainwater is inherently free from the chlorine, fluoride, and other chemicals commonly found in municipal water supplies, offering a more natural hydration source for plants. Its low mineral content is particularly advantageous for sensitive plant species that may react negatively to the salts in tap water.
To optimize a rainwater harvesting system, it’s essential to consider the catchment area’s size, typically the greenhouse roof, and the local rainfall patterns. This information helps in designing a system with adequate storage capacity to meet the greenhouse’s irrigation needs throughout the dry periods.
Additionally, incorporating first flush diverters and filters can improve water quality by removing debris and contaminants before the water enters the storage tanks, ensuring that the plants receive clean, healthy water.
Efficient Irrigation Systems
The implementation of efficient irrigation systems is paramount for the success of earth-sheltered greenhouses. Among the various irrigation methods, drip irrigation stands out for its ability to provide targeted, efficient watering directly to the plant roots. This method significantly reduces water loss through evaporation and runoff, ensuring that every drop of water is used to its fullest potential.
Drip irrigation systems can be customized and scaled to fit any greenhouse size, making them suitable for a wide range of plant types and layouts. By delivering water slowly and directly to the soil, these systems help maintain an optimal moisture level, encouraging deep root growth and improving plant health. Moreover, drip irrigation minimizes the water contact with plant leaves, reducing the risk of leaf diseases and fungal infections that thrive in moist conditions.
Automation is a key feature that enhances the efficiency of drip irrigation systems. Through the integration of timers, soil moisture sensors, and climate controls, the irrigation system can automatically adjust the watering schedule based on the actual needs of the plants. This level of precision ensures that plants are neither overwatered nor underwatered, promoting efficient water use and reducing waste.
Additionally, automated systems can save time and labor, allowing greenhouse owners to focus on other aspects of greenhouse management. By monitoring soil moisture levels and adjusting irrigation accordingly, these systems ensure that plants receive the right amount of water at the right time, optimizing growth conditions and enhancing overall productivity in earth-sheltered greenhouses.
Moisture Control and Drainage
Effective moisture control and drainage are cornerstone elements in the design and maintenance of earth-sheltered greenhouses. These systems are essential not only for managing water use within the structure but also for safeguarding the greenhouse from the potential damages caused by excessive moisture and water accumulation. Here’s a deeper look into the importance of these systems and how they can be implemented:
A robust drainage system is crucial for any earth-sheltered greenhouse, designed to prevent water accumulation that could compromise the structure’s integrity. Excessive moisture can lead to a host of problems, including foundation erosion, increased humidity levels inside the greenhouse, and the potential for mold and mildew growth.
To combat these issues, an effective drainage system beneath the greenhouse floor is often installed to collect and redirect water away from the building. This system might include a combination of drainage tiles, gravel beds, or French drains, which work together to facilitate the flow of water out of harm’s way.
Enhancing the drainage around the greenhouse perimeter is another strategic approach to moisture management. By incorporating gravel trenches or perforated pipes along the edges of the greenhouse, water can be efficiently diverted away from the structure.
This method is particularly effective in areas prone to heavy rainfall or where soil conditions promote water retention. The choice of gravel or perforated pipes should be based on the specific needs of the greenhouse, including the soil type, slope of the land, and average rainfall levels.
To further protect an earth-sheltered greenhouse from water infiltration, the application of moisture barriers and waterproof membranes is recommended. These barriers are applied to the exterior walls and sometimes the roof, serving as an additional layer of protection against moisture.
High-quality waterproof membranes can significantly reduce the risk of water seeping into the greenhouse, thereby preventing the associated problems of dampness, mold, and structural decay. When selecting a moisture barrier or membrane, it’s important to choose materials that are durable, resistant to punctures, and capable of withstanding the soil pressure.
Mulching and Soil Management
Mulching and soil management are integral practices for optimizing water use and promoting plant health in earth-sheltered greenhouses. Let’s delve deeper into how these practices contribute to a sustainable greenhouse environment.
Mulching serves as a critical tool for conserving soil moisture and minimizing the need for frequent watering. By applying a layer of organic material such as straw, wood chips, or leaves atop the soil, mulch acts as an insulating blanket. It slows the evaporation of moisture from the soil surface, thereby maintaining a more consistent soil moisture level. This not only benefits the plants by providing them with steady access to water but also conserves water resources.
Moreover, organic mulches bring the added advantage of enriching the soil as they gradually decompose. This process introduces beneficial organic matter into the soil, improving its structure and fertility.
Enhanced soil structure improves water retention and drainage, making it easier for plant roots to access the nutrients and water they need. Additionally, mulching can help regulate soil temperature, protect against soil erosion, and suppress weed growth, further contributing to the health and productivity of the greenhouse environment.
In earth-sheltered greenhouses, selecting the appropriate soil mix is crucial for achieving the delicate balance between adequate drainage and necessary moisture retention. Soil that drains too quickly may not hold sufficient moisture for plants, while soil that retains too much water can lead to root diseases and poor plant health.
Incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil can significantly enhance its water-holding capacity. This organic matter acts like a sponge, retaining water and releasing it slowly over time, ensuring that plants have a continuous supply of moisture.
Soil management also involves regular assessment and amendment of the soil to maintain its optimal structure and fertility. Periodic testing for pH levels and nutrient content can guide the addition of necessary amendments, ensuring that the soil environment remains conducive to plant growth.
Monitoring and Maintenance
The success of water management techniques in an earth-sheltered greenhouse relies heavily on diligent monitoring and maintenance. Let’s explore these aspects in more detail.
Regularly inspecting the irrigation system for leaks is fundamental to preventing water waste and ensuring efficient use of resources. Even minor leaks can lead to significant water loss over time, so addressing these issues promptly is crucial.
Gutter and downspout maintenance is another critical aspect of water management. Ensuring that these components are clean and free from debris allows for the effective collection and redirection of rainwater, particularly important for greenhouses utilizing rainwater harvesting systems.
The installation of moisture sensors represents a technological advancement in greenhouse management. These sensors provide real-time data on soil moisture levels, enabling precise adjustments to irrigation schedules. This technology ensures that plants receive the right amount of water at the right time, optimizing water usage and promoting plant health.
Regular soil monitoring is also vital. Keeping a close eye on soil conditions, including moisture levels and nutrient content, can help identify the need for adjustments in watering practices or soil amendments. This proactive approach to soil management supports the overall health of the greenhouse ecosystem.
Incorporating these water management techniques can significantly improve the sustainability and efficiency of an earth-sheltered greenhouse. By addressing the challenges of water seepage, drainage, and irrigation, gardeners can create a thriving environment for plants to grow, regardless of the weather conditions outside.
Climate Control Technologies
Effective climate control within earth-sheltered greenhouses is pivotal for creating an optimal growing environment that supports plant health and productivity year-round. Unlike traditional greenhouses, the subterranean design of earth-sheltered greenhouses offers unique advantages and challenges in regulating temperature and humidity. Implementing advanced climate control technologies not only enhances these natural benefits but also addresses potential drawbacks, ensuring a stable environment regardless of external weather conditions.
This section explores several key technologies and strategies for maintaining the ideal climate in an earth-sheltered greenhouse.
Thermal Mass and Passive Solar Heating
The use of thermal mass is a fundamental aspect of climate control in earth-sheltered greenhouses. Materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete, stone, or water barrels, can store heat during the day and release it at night, helping to stabilize temperature fluctuations.
Coupled with strategic orientation for maximum solar gain, passive solar heating can significantly reduce the need for additional heating sources, making the greenhouse more energy-efficient and sustainable.
Geothermal Heating and Cooling
Geothermal systems harness the earth’s stable underground temperature to heat and cool the greenhouse. By circulating water or air through underground pipes, these systems can absorb heat from the greenhouse during hot periods and release it back when it’s cooler.
Geothermal heating and cooling are particularly effective in earth-sheltered greenhouses due to their proximity to the ground, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for year-round climate control.
Automated Ventilation Systems
Proper ventilation is crucial for managing humidity and preventing overheating in earth-sheltered greenhouses. Automated ventilation systems can open and close vents based on temperature and humidity sensors, ensuring adequate air circulation without manual intervention. These systems can be particularly beneficial during the warmer months, allowing excess heat to escape and maintaining a comfortable environment for plants.
Humidity Control Solutions
Maintaining optimal humidity levels is essential for plant health and can prevent issues such as mold and mildew growth. Humidity control technologies, including dehumidifiers and misting systems, can be integrated into the greenhouse’s climate control strategy. By automatically adjusting humidity levels based on real-time measurements, these solutions help ensure that plants receive the ideal balance of moisture in the air.
Smart Greenhouse Controls
The integration of smart controls and monitoring systems represents the forefront of climate control technology in earth-sheltered greenhouses. These systems allow for the centralized management of heating, cooling, ventilation, and humidity, often accessible remotely via smartphone or computer. With real-time data analytics and alerts, greenhouse owners can quickly respond to changes in the environment, optimizing conditions for plant growth and conserving energy.
By implementing these climate control technologies, earth-sheltered greenhouses can achieve an efficient and sustainable growing environment. Each technology offers distinct advantages, and when used in combination, they can provide a comprehensive solution to the challenges of maintaining a stable climate, ensuring the success of the greenhouse operation.
Conclusion
Building an earth-sheltered greenhouse offers a sustainable and energy-efficient solution for year-round gardening, harnessing the earth’s natural insulation to moderate internal temperatures. This innovative approach not only reduces energy costs but also supports a more eco-friendly way of producing food, enhancing biodiversity and promoting local food security. With the integration of advanced water management and climate control technologies, gardeners can enjoy high yields and optimal plant health in an aesthetically pleasing and environmentally conscious setting.









