Last Updated on July 9, 2025 by teamobn

The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates over 90 different contaminants in drinking water, out of 85,000 toxic chemicals. Shocking, right? So, how do households protect themselves from these contaminants lurking in the waters? Whole house water filtration systems!
Investing in a filtration system is a significant decision. So, do your research before getting one. Ask these questions:
- What are my water goals? Free of sediment? Free of bacteria? Soft?
- What is my budget?
- What contaminants plague my water supply?
In this ultimate guide, we will discuss the different types of whole house filters. We will also discuss the contaminants they target and the pros and cons of each technology.
Contents
Tank-Based Systems vs Cartridge-Based Systems
The two common types of whole house water filtration systems are:
- Tank Based Systems
- Cartridge Based Systems
Let‘s compare these two systems:
Tank-based filtration systems
For tank-based systems, water first passes through a pre-filter, after which it goes through a semi-permeable membrane. Now, after the water has been filtered, it is stored in a pressurized tank. This means you can enjoy a continuous flow of clean, filtered water into your home.
Tank-based systems also have some drawbacks to consider:
- Installation: They often require more complex installation than cartridge systems. So, you may need to employ the services of professionals.
- Space Constraints: The tanks are big and will require dedicated storage space in your house.
- Wastewater Production: The Reverse Osmosis (RO) process generates wastewater that needs to be drained. This could impact your water bill over time.
Cartridge Based Systems
Cartridge-based systems are simpler and compact. Here, your water flows directly through the filter cartridge, losing contaminants as it passes. There is no tank involved, so replacement is quick and simple.
Cartridge-based systems offer several filtration media that focus on specific contaminants, including chlorine, lead, and impurities that compromise taste.
However, cartridge-based systems also have limitations:
- Since they have lower capacity than tank-based systems, you may need to replace them more frequently depending on your usage.
- Cartridge-based systems don’t come with tanks, so you won’t have a reserve of filtered H20. Plus, the flow may be slower compared to tank-based systems.
Overall
Consider your priorities;
Would you prefer access to the large volume of filtered water, even if it requires more space and a complex setup? Then go for the tank-based systems.
Or are you looking for a space-saving, easy-to-replace option that targets specific contaminants? The ideal system for you is the cartridge-based system.
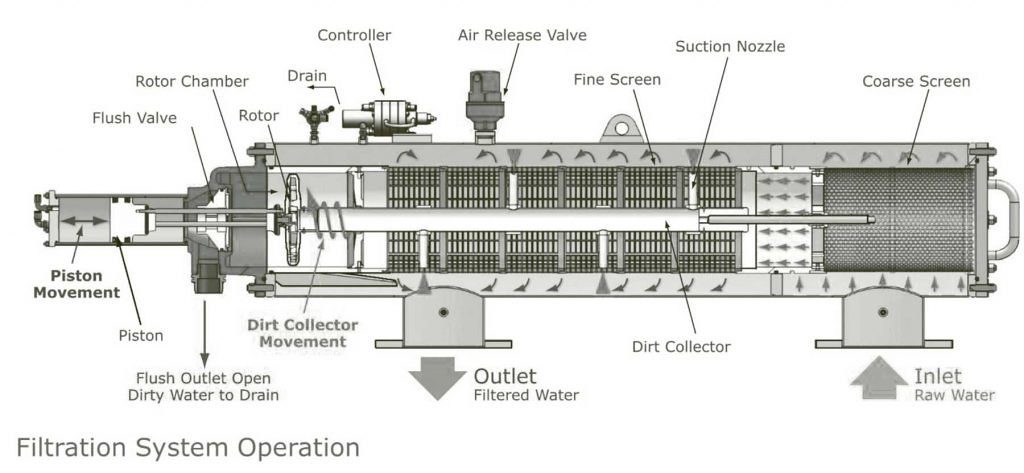
Every Type of Whole House Water Filter System, From Most to Least Common
Here are the whole house water filter types, from the most to least common.
Note that your unique water properties and the contaminants in your supply should inform your filtration system.
Catalytic Activated Carbon Filter Systems
The Catalytic Activated Carbon filter system comprises activated carbon and a catalyst. The activated carbon is a porous material that holds contaminants like chlorine as H20 passes through.
The catalyst promotes the breaking down of chloramines commonly used as a disinfectant in municipal water treatment. However, chloramines can have an unpleasant taste and odor.
Pros
- CAC filters eliminate chlorine and chloramines.
- Some CAC filters also reduce volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- CAC filters last longer than other types of house filters, depending on your water quality.
Cons
- While they are effective for chlorine and taste improvement, CAC filters do not eliminate other contaminants like lead or heavy metals.
- CAC filters are often more expensive than basic carbon filters.
Who is CAC Filter Good For?
CAC filtration offers taste improvement and a potentially longer lifespan. It is a great choice if:
- You are most concerned about eliminating chlorine taste and odor,
- Your water source doesn’t have a significant amount of heavy metals.
However, if your supply contains more contaminants, you might need to explore other robust filter types.
UV Purifiers
Other whole-house filtration systems physically trap contaminants. However, UV purifiers take a unique approach. They use short-wavelength ultraviolet light to target and inactivate harmful microorganisms like bacteria/ viruses and cysts.
How it Works
The water that flows through the UV purifier is exposed to a potent quantity of ultraviolet light. This light alters the DNA of microorganisms, making them unable to reproduce. The inactivated microorganisms are then safely flushed away with the filtered water.
Benefits of UV Purifiers
- UV purifiers remove bacteria/ viruses and cysts from your water.
- The purification doesn’t employ disinfection chemicals like chlorine. This ensures that the H20 is tasteless and odorless.
- They are low maintenance, You may only be required to do an occasional bulb replacement.
Cons
- UV purifiers target microorganisms. So, they don’t remove dissolved chemicals or physical contaminants like chlorine, taste, or odor.
- UV light is most effective in clear H20. Prefilter if your water is heavily sedimented or cloudy,
Are UV Purifiers Right for You?
UV purifiers are ideal for households with bacteria or viruses in the supply, especially if you want a chemical-free disinfection method.
However, consider your quality concerns and combine UV purification with another filter type for a more comprehensive system.
Whole Home Reverse Osmosis Filtration System
This is how this filtration system works: Firstly, the H20 goes through pre-filters. The pre-filters are designed to remove larger particles like sediments and chlorine. Then, H20 (now pressurized) is forced through the RO membrane, allowing pure H20 molecules to pass through. The membrane rejects dissolved contaminants like minerals, heavy metals, and some bacteria and viruses and sends them to a drain line.
Some RO systems also include a final filtration stage with additional carbon filters to improve taste and odor.
Benefits of Whole Home RO Systems
- RO systems offer the most comprehensive filtration for home treatment. They remove several contaminants, including heavy metals. They also eliminate minerals, chlorine, and even some microorganisms.
- As they eliminate minerals and other dissolved solids, RO systems significantly improve the taste and odor.
- Filtered H20 with RO systems are suitable for drinking, cooking, washing dishes, and even bathing.
Cons
- Whole home RO systems are more expensive to purchase and may require professional installation.
- The RO process generates wastewater that should be drained.
- RO filtration removes many minerals, including some that can be beneficial for health.
Is a Whole Home RO System Right for You?
RO system is a perfect robust water filtration for your household. However, if you only want to improve the taste and odor of your drinking water, get a cost-effective option.
Ultrafiltration
UF membranes employ a size-exclusion process. They act like a microscopic sieve that selectively allows H20 molecules through. However, they hold out larger contaminants.
How it Works
The pressurized water flows through an Ultrafiltration membrane with small pores. These pores often measure around 0.001 microns. They are large enough for H20 molecules to pass through. However, it holds:
- Microscopic contaminants like bacteria/ parasites and some viruses.
- Larger impurities including, sediments, and rust.
Benefits of Ultrafiltration Filters
- UF filters eliminate bacteria, viruses, and cysts.
- They also remove larger particles to improve the clarity of water.
- Unlike RO systems, UF filters don’t remove most dissolved minerals from your water.
Cons
- While effective against microorganisms and larger particles, UF filters don’t remove dissolved contaminants like chlorine, lead, or chloramines.
- UF membranes require occasional cleaning or replacement.
Who Is Ultrafiltration Right for?
Ultrafiltration whole house filter is perfect if your H20 supply has bacteria or parasites. It also preserves the mineral content in the water.
Calcite Filters
As hard water flows through the calcite filter, ion exchange occurs. The calcium and magnesium ions in the hard water are exchanged with sodium ions (all positively charged) released by the calcite system. Thus, effectively reducing the hardness. As the filtration media removes the excess calcium and magnesium, calcite filters can improve the taste of your water, making it less bitter or metallic.
Benefits of Calcite Filters
- Calcite filters are cost-effective and a method of softening hard water.
- It eliminates the bitterness or metallic taste associated with hard water.
- Calcite filters prevent scale buildup in the water outlets in your home.
Cons
- Calcite filters mostly target hardness so they are not effective against other contaminants like chlorine or bacteria.
- As the Calcite becomes saturated with hardness minerals, it would lose its effectiveness. So you would need to regularly replace the filters.
- Calcite may slightly increase the pH of your H20, making it more alkaline.
Is a Calcite Filter Right for You?
Calcite filter is the best bet for your household if:
- You are on a budget
- You are looking for a solution for hard water
Conclusion
With the right information, you can find the perfect whole house water filtration system for you and your family. This will ensure that your households get clean, and refreshing filtered water from your outlets.
Remember, the perfect choice depends on your water quality concerns and desired level of filtration.






